

|
Joshua Gibson
14/2/05

What energy is
Energy is something we can use to make electricity and heat for homes and factories. It can also be used power transport. It comes in many forms, such as oil, coal, gas, wind, tidal/wave, geo-thermal, solar and nuclear.
Difference between non-renewable and renewable energy
The different forms of energy can be split into non-renewable and renewable. Renewable energy is energy that can’t run out. For example, every time the sun rises solar power is available. Non-renewable energy can run out. Once a coal mine is empty there is no more coal available, once all the coal mines are empty there will be no more coal left.
Where non-renewable energy comes from
Coal, oil and gas are fossil fuels; this means that they were formed in prehistoric times from plants and other living things. Over millions of years, the remains of these prehistoric plants became crushed and eventually became fossilised. Nuclear energy is a non-renewable source of energy because it too can run out. Uranium mines can become exhausted even though there is plenty of uranium fuel available now.
Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels were formed by prehistoric dinosaur bones, plants and organisms that lived in ancient seas and rivers. Over a long period of time the bodies of these organisms have been pushed down into the swamps by their own weight.. Slowly dead animal bones and plants began to fall on top of each other pushing the older plants deeper. Gradually other sediments built up over them crushing and squeezing the plant and animal fragments turning them into fossil fuels.
Coal, oil and gas were formed by different conditions of time, pressure and temperature.



Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is the energy released when atoms are either split or joined together. Atoms are made up of three major particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. The most common fissionable atom is an isotope of uranium 235 known as (U235), which is the fuel used in most types of nuclear reactors today. Once uranium is mined the U-235 must be taken out and processed before it can be used as a fuel. When it is ready to be used, the nuclear fuel will be the form of a pellet about one inch long. The pellet makes the same amount of electricity as one tonne of coal.
Oil
Oil is formed from the remains of tiny plants and animals plankton that died in ancient seas between 10 million and 600 million years ago. After the organisms died, they sank into the sand and mud at the bottom of the sea.
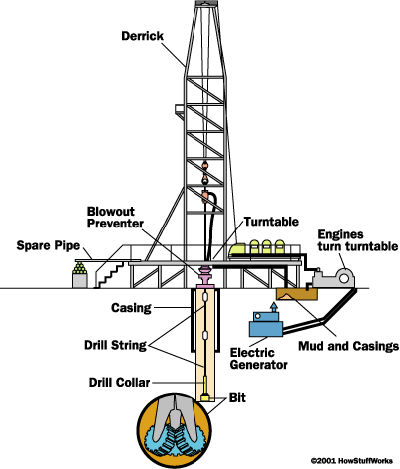
Oil is a thick black liquid and is a fossil fuel. An oilrig is a machine that drills into the ocean to search for oil. Oil is trapped underground in the rocks like water trapped in a sponge. There are also land oilrigs that sit on the surface and do the same as ocean rigs. Tar has been used for many centuries but it was not until the 1850’s that the first oilrigs began to be made.
Gas:
Gas is a fossil fuel. It is used for all kinds of things like BBQ, fires in old houses. Gas is made the same way as petroleum and is also trapped between layers of rock. Natural gas is trapped, compressed and piped into homes to be used in stoves and hot water systems. LPG gas is made from crude oil. It is used for cooking and heating in homes, industrial heating in boilers, kilns and furnaces, and for camping and caravanning appliances. LPG can also be used as an alternative to petrol as an engine and transport fuel. Using LPG reduces greenhouse gas emissions from a vehicle by up to 20 percent. Natural gas was not used until the 20h century due to the difficulties in extracting and transporting it. Coal gas which is produced from heating coal has been used for heat and light since Victorian times.

Coal:
Coal is a black rock, which comes from a coal mine. There are different types of coal mine. Thermal coal which is used in power stations and cokeing coal which is used for industrial processes such as refining iron into steel. It can be mined by digging a mineshaft down into the ground to the seam of coal. This is a layer of coal deep under ground. Miners dig the coal out of the seam it is carried to the surface where it is crushed and put on to trains and taken to where is can be used. Other types of mining are used when the coal is nearer the surface. Today much coal is obtained by the open-cut method, if there is not too much rock and soil on top of the coal seam. It can be taken away and the coal is cut out in shelves that slope inwards. Huge trucks drive up and down these shelves to take out the coal. A more recent approach is strip mining. This involves cutting a narrow strip and when all the coal is removed from it, a strip is cut next to the first strip. The rock and soil from this second strip is used to fill the previous strip. In this way, the mined area is being reused as a park or a field.
Nuclear:
Nuclear power is not a fossil fuel. Energy in the form of heat is given off in a nuclear reaction. This is a very powerful fuel, a single fuel rod may last up to 4 years, producing a large amount of electricity. Due to the large size of a nuclear reactor, nuclear power is not easily transported. It is usually found in large power stations such as Hunterston in Ayrshire. It is also used to power nuclear submarines and aircraft carriers.

Where they are likely to be used
|
Heating
|
Electricity
|
Transport |
Cooking |
|
|
Oil:
|
3
|
4
|
8 |
0 |
Gas:
|
9
|
8
|
2 |
8 |
Coal: |
7
|
7
|
0 |
1 |
Nuclear: |
1 |
9 |
2* |
0 |
Key 0=not important 10= very important,
*= nuclear submarines
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
Oil
Oil is easily extracted from the ground using oilrigs. It can be transported in bulk using pipelines, oil tankers, and lorries. It provides lots of different types of fuels, from fuel oil for ships, petrol, diesel, LPG and many other products such as lubrication oil, plastics and tar. Oil is very useful for transport because there is a lot of energy in a small space. Cars and lorries can use diesel and petrol to power their engines instantly because it is used directly in the engine. A car with a tank full of petrol can go a long way, because petrol contains a lot of energy.
Gas
Like oil natural gas is easily extracted for the ground using drilling rigs. It can be piped to its destination and unlike oil it does not require any processing before use.
It can be used in engines like petrol but it can be dangerous because it could cause an explosion. It is relatively cheap and can easily be stored.
Coal
Coal is plentiful, with supplies for many hundreds of years still in the ground; it is easily mined and is cheap.
Nuclear
Nuclear power does not cause pollution or greenhouse gasses. It also creates a lot of electricity as well. There is a lot of nuclear fuel to last us for about another 8 years.
Disadvantages
Oil
There is not much oil left in world. It is expected to run out some day in the next 50 years. It is very expensive, because it is becoming increasingly rare. It causes pollution, coast lines and beaches become polluted from the spillage of oil from oil tankers such as Exxon Valdez. When oil is burned as a fuel in cars and lorries it comes out of the exhaust pipe containing polluting gasses.
Gas
Gas, being a hydrocarbon, suffers from the same problem of depletion as oil. Otherwise, the main disadvantage is that it is not as easy to transport, requiring either pressure pipelines or special ships which pre-process it into LNG (liquefied natural gas). Both of these are at great risk to terrorism (a fully loaded LNG ship is apparently equal to 55 Hiroshima nuclear bombs). Gas is best used for electricity production and heating, it cannot supply the fuels and products that oil is used for. Conversion to a fuel suitable for aircraft and ships uses large amounts of energy and money.
Coal
Coal is difficult and expensive to mine, not to mention all the dangers and hazards, which are involved.The dust from coal can cause respiratory problems such as black lung disease if it is inhaled.The burning of coal releases a high amount of sulphur. This contributes to the environmental pollution.
Nuclear
Nuclear fuel uses Uranium, one of the rarest elements in nature. Uranium is a non-renewable resource. It is very expensive to build nuclear plants. The dangers of steam explosions from failures in the cooling systems are potential hazards. Too much exposure to the radiation can be fatal or cause cancer. Nuclear power produces wastes which are still radioactive and dangerousfor a long time after they have been used.
Local energy non-renewable energy sources
There are currently 3 nuclear power stations operating in Scotland. Two of them are owned and operated by British Energy. They are at Hunterston and Torness. The third is owned and operated by BNFL. This is at Chapelcross.
Scotland once had a very large numbers of coal mines, in several large and numerous small coalfields, most of which were in the 'central valley' between Edinburgh and Glasgow, or a little to the north of this. Smaller coalfields were worked elsewhere, as for example in Ayrshire. By 1991 there was only one large deep coalmine left in operation at Longannet near Kincardine in Fife. The market park where the cars are parked was once a coal refinery, which made coal gas for Crieff.
Scotland has a lot of oil under the North Sea. Aberdeen is the centre of the oil industry in Scotland.
Bibliography
Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy
